Therapy in medical settings is a cornerstone of modern healthcare, offering a diverse range of therapeutic interventions aimed at addressing physical, emotional, and cognitive health concerns.
From medication management and physical rehabilitation to psychotherapy and holistic approaches, therapy plays a vital role in promoting healing, recovery, and overall well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various types of therapy offered in medical settings, their benefits, and their crucial contributions to enhancing health and quality of life.
Table of Contents
ToggleTypes of Therapy in Medical Settings:
- Medication Therapy: Medications are commonly prescribed to manage a wide range of health conditions, including chronic diseases, mental health disorders, and acute illnesses. Medication therapy aims to alleviate symptoms, control disease progression, and improve overall health outcomes.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapists use specialized exercises, manual techniques, and modalities to rehabilitate injuries, improve mobility, and alleviate pain. Physical therapy is essential for individuals recovering from surgeries, accidents, or chronic conditions affecting their musculoskeletal system.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapists focus on helping individuals regain or develop the skills needed to perform daily activities and participate in meaningful occupations. They work with patients to address physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges that may impact their ability to function independently.
- Speech Therapy: Speech-language pathologists assist individuals with communication and swallowing disorders, providing interventions to improve speech, language, voice, fluency, and swallowing abilities. Speech therapy is crucial for individuals recovering from strokes, traumatic brain injuries, or developmental delays.
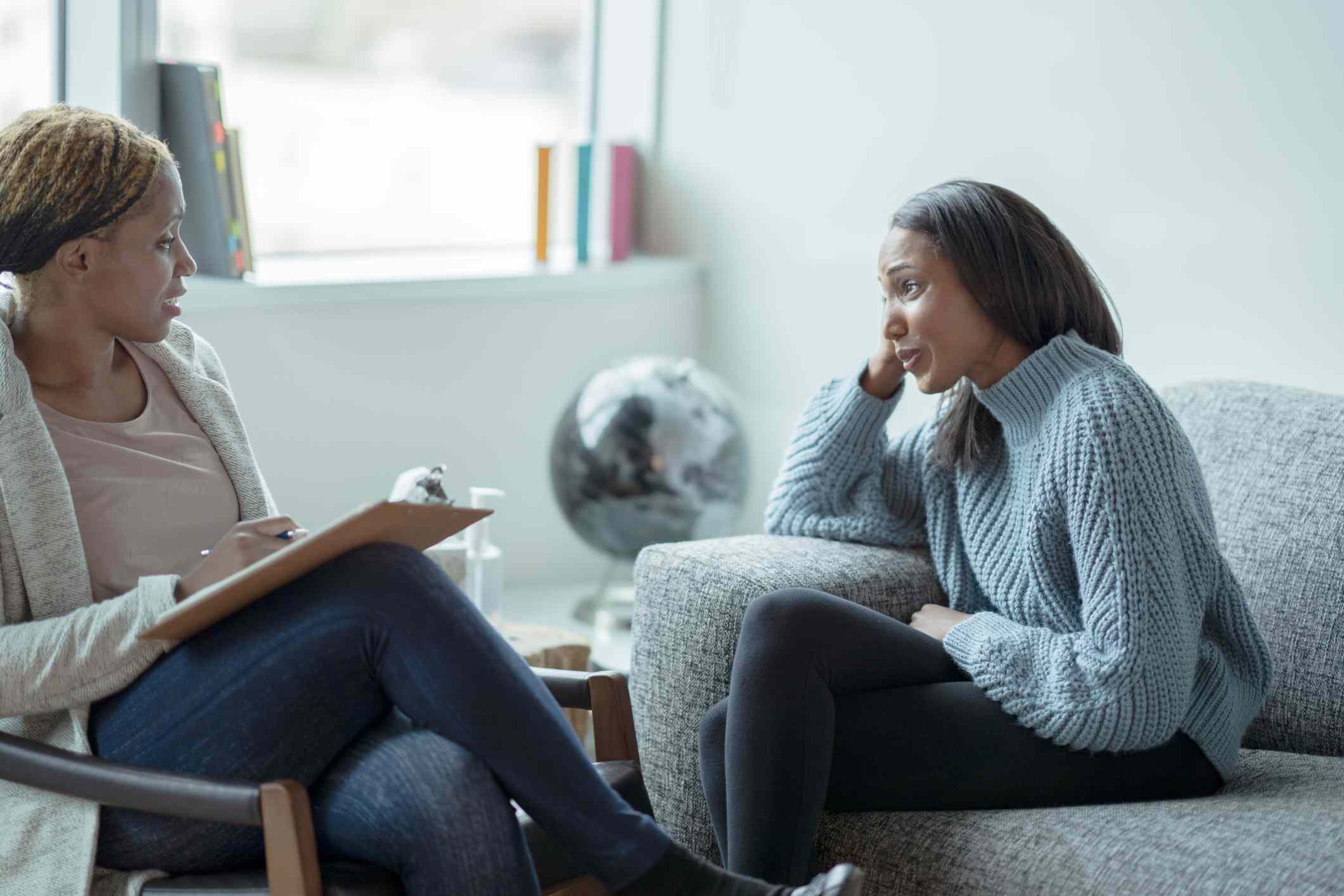
- Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a therapeutic intervention used to treat mental health disorders, emotional distress, and interpersonal issues. Through structured sessions with a trained therapist, individuals explore their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors to gain insight and develop coping strategies.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is effective in treating anxiety disorders, depression, PTSD, OCD, and other mental health conditions by helping individuals develop healthier ways of thinking and responding to stressors.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with concepts of acceptance and mindfulness to help individuals regulate emotions, manage distress, and improve interpersonal relationships. It is particularly effective in treating borderline personality disorder and other mood disorders.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a specialized form of therapy used to process traumatic memories and alleviate symptoms of PTSD and trauma-related disorders. By facilitating bilateral stimulation of the brain, EMDR helps individuals reprocess distressing experiences and reduce emotional reactivity.
- Art Therapy: Art therapists utilize creative expression as a therapeutic tool to promote emotional healing, self-exploration, and personal growth. Through various art modalities such as painting, drawing, and sculpting, individuals can communicate and process complex emotions in a nonverbal manner.
- Music Therapy: Music therapists harness the power of music to address physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs. Through singing, playing instruments, and listening to music, individuals can improve mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall well-being.
Benefits of Therapy in Medical Settings:
- Comprehensive Care: Therapy interventions address the physical, emotional, and cognitive aspects of health, providing holistic support for individuals facing complex medical and mental health challenges.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Therapy contributes to improved health outcomes by managing symptoms, promoting recovery, and enhancing overall well-being, leading to better quality of life for patients.
- Enhanced Functioning: Therapy helps individuals regain or improve their ability to perform daily activities, communicate effectively, and engage in meaningful occupations, fostering independence and autonomy.
- Pain Management: Therapeutic interventions such as physical therapy, relaxation techniques, and psychotherapy help alleviate pain, reduce reliance on pain medications, and improve overall pain management strategies.
- Emotional Support: Psychotherapy and counseling offer emotional support, validation, and coping strategies for individuals experiencing mental health challenges, trauma, grief, or life transitions.
- Skill Development: Therapy interventions equip individuals with coping skills, communication strategies, problem-solving abilities, and adaptive behaviors to navigate challenges and achieve personal goals.
- Preventive Care: Therapy serves as a preventive measure, helping individuals identify risk factors, develop healthy habits, and address early signs of health problems before they escalate.
In conclusion, therapy in medical settings encompasses a diverse range of therapeutic interventions aimed at promoting healing, recovery, and overall well-being. By addressing the physical, emotional, and cognitive aspects of health, therapy empowers individuals to achieve optimal health outcomes and lead fulfilling lives.
Whether managing chronic conditions, recovering from injuries, or addressing mental health concerns, therapy plays a crucial role in enhancing health and quality of life for patients across the lifespan.